Human neutrophil assays
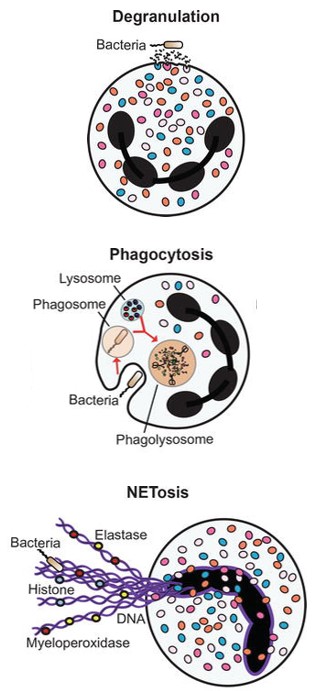
Neutrophils, the predominant leukocyte population in peripheral blood, are recognized as the primary line of defense against pathogens. They employ various mechanisms, including phagocytosis, granule release, and formation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), to eliminate invading microorganisms. Furthermore, neutrophils possess the ability to alter their phenotype and subsequently function in response to inflammatory stimuli. Additionally, emerging evidence suggests that neutrophils can modulate both innate and adaptive immune responses through direct and indirect interactions with other immune cells. Apart from their protective roles, neutrophils have also been implicated in disease progression. Specifically, NETs have been implicated in thrombosis, gout and venous atherosclerosis. Moreover, elevated levels of circulating neutrophils have been correlated with tumor advancement and unfavorable prognosis across various cancer types. Given their significant contributions to host defense as well as disease pathogenesis processes, targeting neutrophils represents an ideal approach for developing novel therapeutic strategies.
Our human neutrophil assay Services Include:
At PicoImmune, our scientists routinely screen compounds for their ability to modulate neutrophil function. A typical workflow includes:
- Primary neutrophil isolation or whole blood collection (varies with assay)
- Evaluation of neutrophil purity after isolation: CD66b and CD16 expression
- Test compound treatment
- Stimulation of pre-treated neutrophils (necessity varies with assay): Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate/ A-23187/ n-Formylmethionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine ( fMLF)
- Readout quantification: Reactive oxygen species generation, NETosis, phagocytosis, etc.
human Basophil Assays
CD34+ blood precursor-derived mast cells: purity
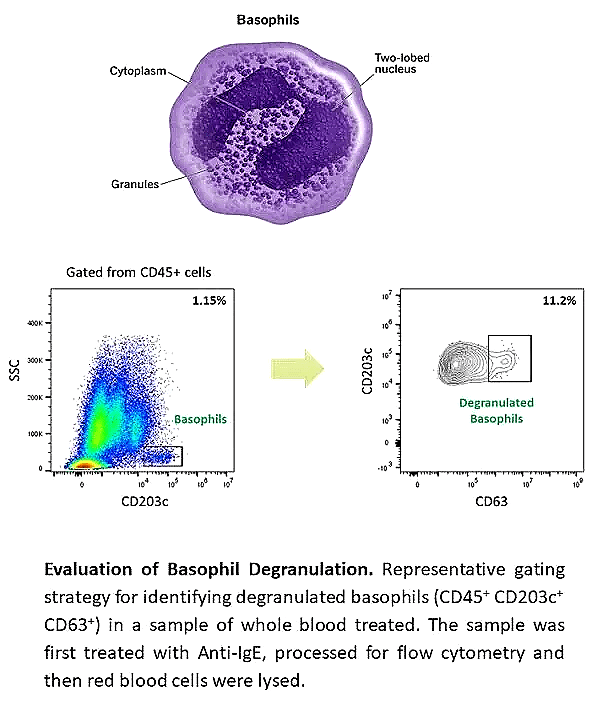
Basophils are peripheral blood leukocytes that are generally associated with type 2 immune responses. They develop within the bone marrow from blood progenitors and enter circulation as mature cells. Like mast cells they express the high affinity IgE receptor, FcεR1 and can be activated by crosslinking of FcεR1-bound IgE-antigen complexes. Human basophils are also known to constitutively express human IL-3 receptor α chain (CD123) and CD63 and CD203c upon activation. They are potent IL-4 and IL-13 producers and consequently implicated in enhancing or polarizing the adaptive immunity. In addition to their protective immune functions, basophils can also induce and exacerbate allergic inflammation when aberrantly activated. Allergic disease is a significant public health problem in developed countries but there are limited therapeutic and diagnostic interventions.
Our basophil assay services include:
The basophil activation test (BAT) has emerged as a useful tool to study allergic disease. The effect of stimuli on the activation state and degranulation of isolated peripheral blood basophils is evaluated by flow cytometry.
BATs are useful for several reasons:
- In vitro model for allergy drug discovery
- Potentially a biomarker of clinical response to treatment
- Ability to explore possible underlying mechanisms at the effector cell level
- Can confirm eligibility of patients for allergy therapy
Our scientists routinely perform BATs using a variety of test articles to discern any potential immunomodulatory activity.
A typical workflow includes:
- Treatment of whole blood with test compounds (fMLF, or anti-human IgE can be the stimulation controls; wortmannin or staurosporine can be the inhibitor control for anti-IgE-induced degranulation)
- Cell staining of CD123, IgE (basophil markers); CD63 (degranulation marker); CD203 (activation marker)
- Flow cytometric analysis of basophil activation and degranulation following red blood cell lysis
Human eosinophil assays
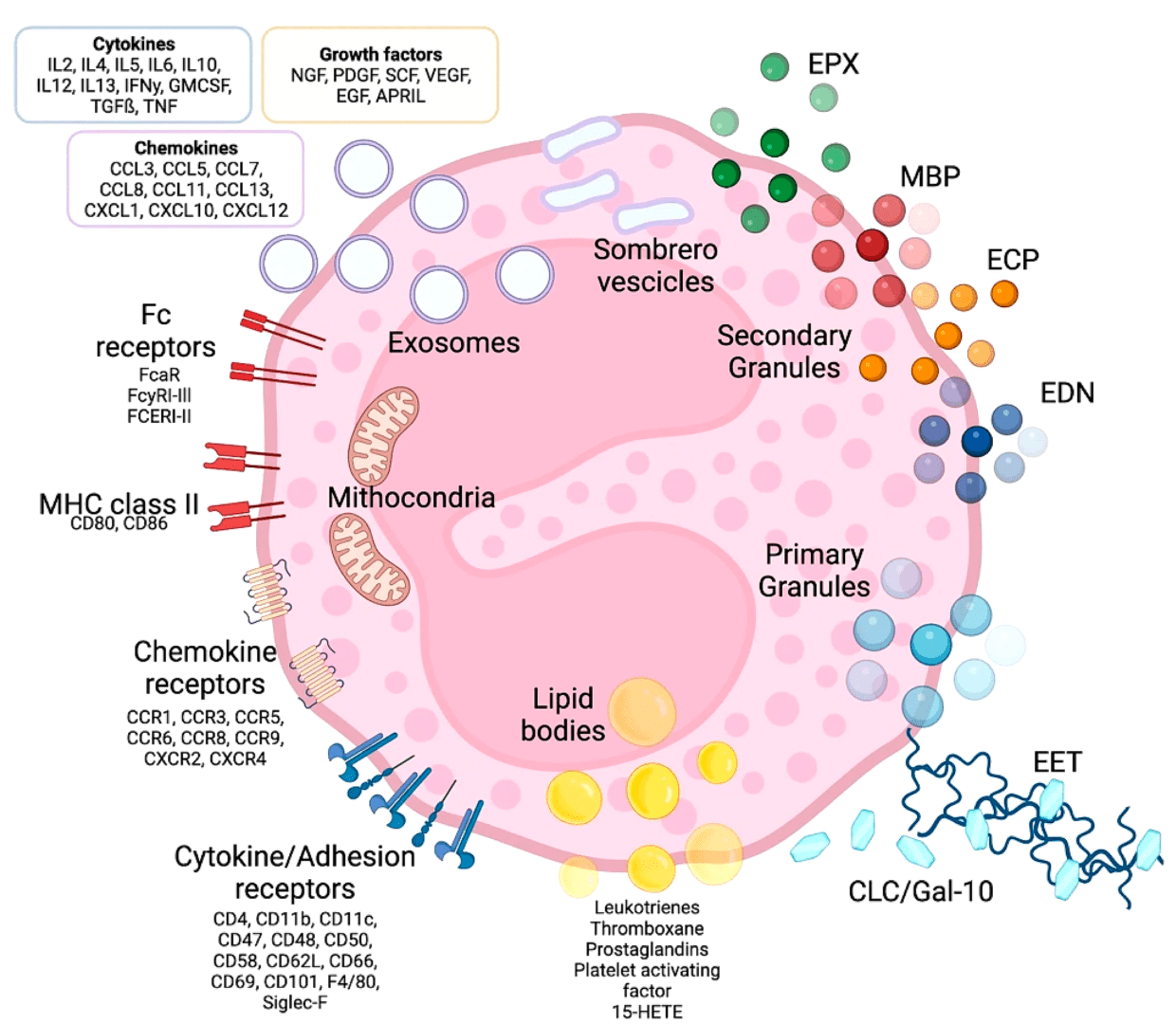
Eosinophils are granular myeloid immune cells primarily localized in tissues, with only a few present in peripheral blood. They are well recognized for their protective response against helminths. The cytotoxic functions of eosinophils rely on the major basic and cationic proteins contained within their abundant cytosolic granules. Despite playing a prominent role in host defense, eosinophils contribute to the pathogenesis of several diseases including allergies, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and colitis, where they induce significant tissue destruction. For instance, severe asthma has been shown to be associated with the accumulation of numerous activated eosinophils near bronchial epithelium causing marked structural damage. Given their involvement in both host defense and disease progression, eosinophils represent an ideal target for developing novel therapies.
Our human eosinophil assay services include:
At PicoImmune, our scientists routinely screen compounds for their ability to modulate eosinophil function.
A typical workflow includes:
- Primary eosinophil isolation from whole blood
- Evaluation of eosinophil purity after isolation: CD66b and CD16 expression
- Test compound treatment
- Stimulation of pre-treated eosinophils (necessity varies with assay)
- Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate / A-23187
- Cytokines (IL-4, IL-13, Eotaxin, etc)
- Platelet-Activating Factor (PAF)
5. Readout quantification:
- Extracellular trap formation
- Degranulation (Eosinophil Peroxidase)
- Cytokine production (IL-3, IL-9, IL-13, IL-5, FGF, GM-CSF, PDGF, CCL5, CCL11, CCL17, etc)
