Human Mast cell Assay
- Mast cells, belonging to the myeloid lineage of immune cells, are distributed in connective tissues throughout the body. The activation and degranulation of mast cells play a significant role in modulating various physiological and pathological conditions.
- In terms of normal physiological functions, mast cells are involved in regulating vasodilation, maintaining vascular homeostasis, mediating innate and adaptive immune responses, promoting angiogenesis, and facilitating venom detoxification.
- Conversely, mast cells have also been implicated in the pathophysiology of numerous diseases such as allergy, asthma, anaphylaxis, gastrointestinal disorders, various malignancies, and cardiovascular diseases.
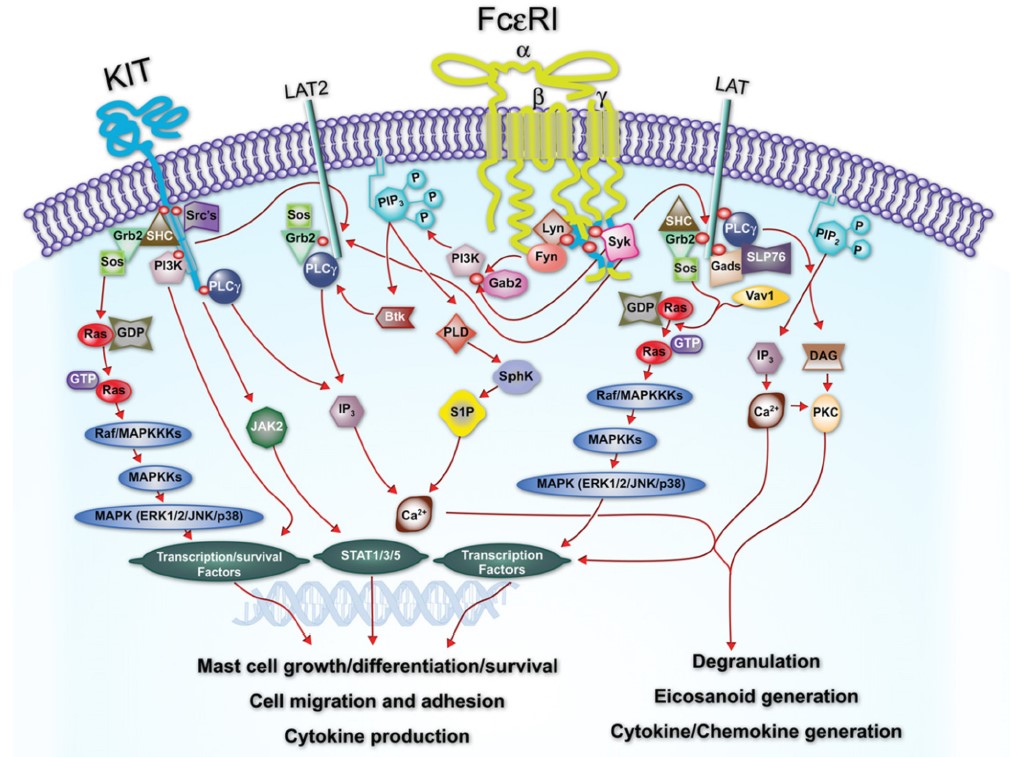
- Mast cells express c-kit and FcεR1 receptors. Human mast cells can be classified into two phenotypes: mucosal mast cells that exclusively produce tryptase and connective tissue mast cells that produce chymase along with tryptase and carboxypeptidases.
- The cytoplasm of a mast cell contains 50-200 large granules which store inflammatory mediators, i.e. histamine, heparin, a variety of cytokines, chondroitin sulfate, and neutral proteases.
- Mast cell activation can occur through antigen/IgE/FcϵRI cross-linking as well as stem cell factor-induced c-kit dimerization.
Human primary mast cell degranulation assay
OUR HUMAN MAST CELL ASSAYS WIDELY USED TO SYUDY BIOLOGY OF DISEASES
- Allergy
- Anaphylaxis
- Asthma
- IgE-mediated hypersensitivity reactions
- Mastocytosis
- Anti-helminth immunity
- Mast cell activation syndromes
- Cancer
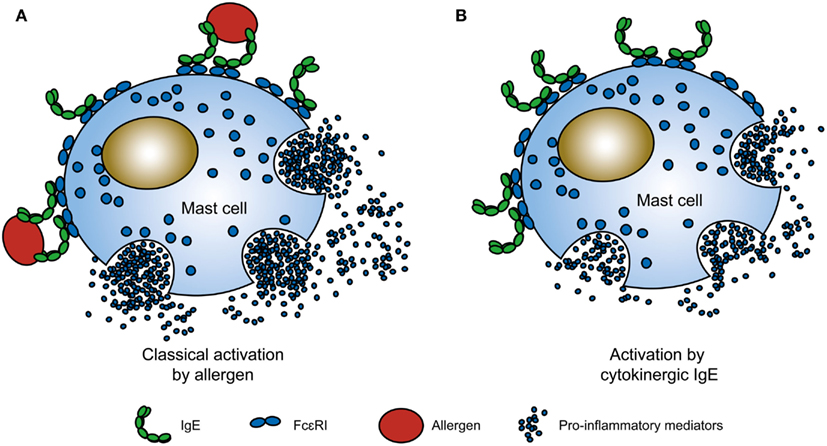
Challenges of Mast Cell Research
- Primary human mast cells are rare in peripheral blood and tissue isolation protocols yield low cell quantities, viability and purity.
- Differentiation of blood stem/precursor cells to mature mast cells is time-consuming and culture reagents are costly.
- Both human (HMC-1, LAD2, LUVA) and rodent (P815, RBL-1, FMA-3) mast cell lines exhibit aberrant phenotypes, including lack/loss of functional receptors such as FcεR1, impaired cytokine production, long doubling time or insufficient cytosolic granules.
Our Service Features
- CD34+ blood precursor-derived mast cells: Mimic mature human mast cells; express functional c-kit and FcεR1; have a well condensed non-lobate nucleus and abundant cytosolic granules
- Variety of readouts: histamine release assay/ tryptase/β-hexosaminidase/cytokines/PGD2/gene expression
- Degranulation Induction: IgE-dependent and -independent (Compound 48/80, cortistatin-14, substance P)
- High throughput: 96/384-well format, duplicate or triplicate; multiple donors can be tested concurrently; highly multiplex analysis at transcriptome/ secretome/proteome levels
- Robust and highly reproducible: More predictive results than with cell lines or rodent cells
- Well-validated reagents and protocol: provide established differentiation reagents, mast cell agonists and antagonists.
How Does Our Assay Work?

- CD34+ precursor cell isolation from peripheral blood.
- Differentiation of CD34+ precursor to mature mast cells
- Evaluation of mast cell culture purity: c-kit and FcεR1 expression
- Test compound treatment during stimulation
- Readout quantification:
- Cytokines production
- Gene Expression
- Degranulation products/markers (histamine release assay, etc.)
human mast cell degranulation assays Example Data
CD34+ blood precursor-derived mast cells: purity
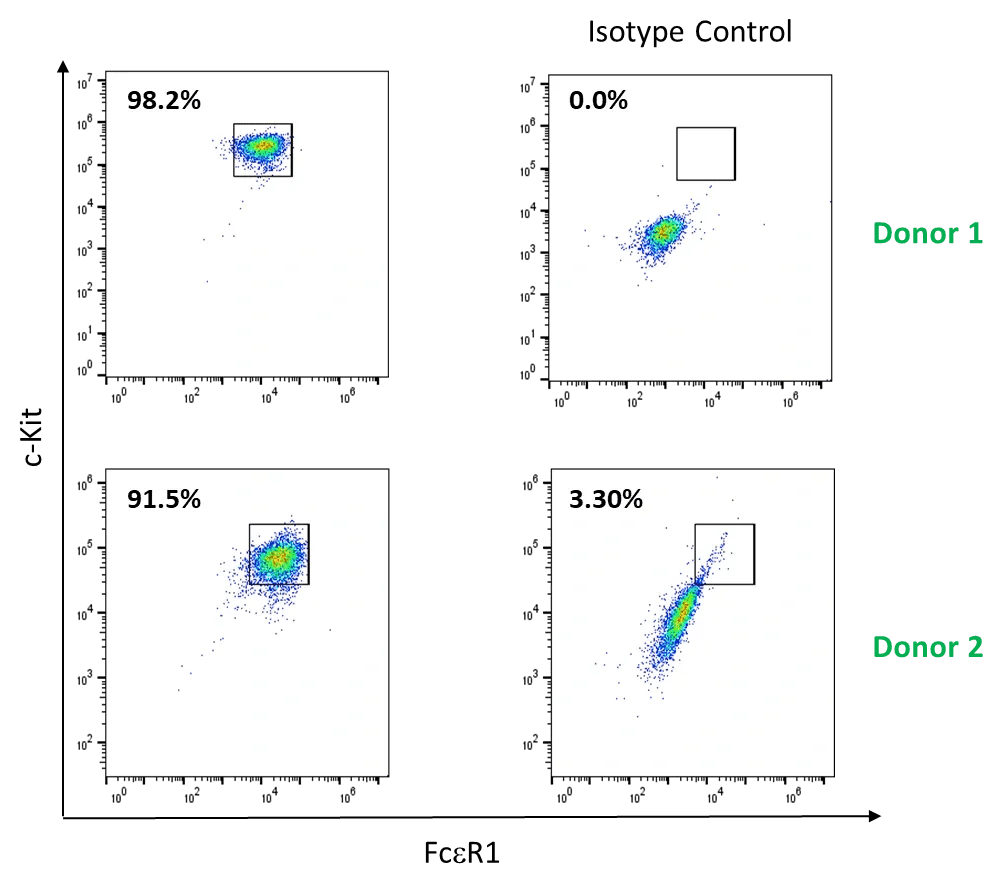
- Primary CD34+ hematopoietic precursor cells isolated from 2 healthy donors were differentiated to mast cells in vitro by culturing cells in medium supplemented with recombinant stem cell factor (SCF), interleukin (IL)-6, and IL-3. Mast cell culture purity was evaluated after weeks of differentiation based on the expression of c-kit and FcεR1 with flow cytometry.
Compound 48/80 induced mast cell degranulation
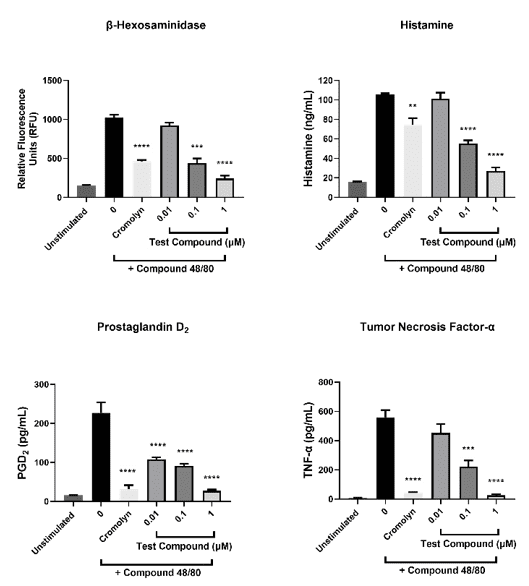
- Mature CD34+ hematopoietic precursor-derived mast cells were incubated with varying concentrations of test compound or cromolyn (mast cell stabilizer) during stimulation with compound 48/80 (mast cell activator). After treatment, β-hexosaminidase, histamine, prostaglandin D2 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α in the cell-free supernatants were quantified. Data shown are mean ± SEM (3 donors).
